Monitoring blood sugar levels is a full-time job; sometimes, glucose meters help you closely monitor your sugar levels as you would like. This is where a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) comes in. A CGM is an FDA-approved device that helps you track your blood glucose levels during the day and night. It automatically records blood sugar levels in 5 to 15-minute intervals.
It is excellent in helping you detect patterns and trends to help give you and your doctor a clear picture of your condition. The data collected helps to manage and control the condition betters.
How Does A CGM Work?
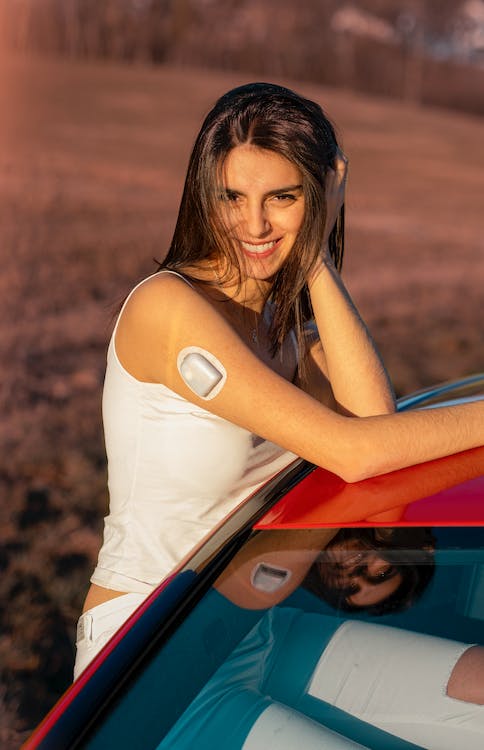 The device measures the amount of sugar or glucose in the fluids inside your body. It uses tiny sensors placed under the skin of your stomach or at the back of your arm. The process is painless. The sensor’s transmitter sends information to a wireless pager often clipped around the belt.
The device measures the amount of sugar or glucose in the fluids inside your body. It uses tiny sensors placed under the skin of your stomach or at the back of your arm. The process is painless. The sensor’s transmitter sends information to a wireless pager often clipped around the belt.
The monitor is programmed to display the glucose in intervals of 1, 5, 10, or 15 minutes. If your blood glucose levels fall dangerously low or too high, the monitor on your belt will alarm you to take action.
Previously, only doctors could read the CGM systems’ data, but that has changed. Now anyone with the device can read the data as part of the at-home care plan. Additionally, you can download the data on your tablet, smartphone, or your computer to see the trends and patterns in your glucose levels
Your doctor uses the information to come up with an efficient diabetes care plan which includes:
- Your dosage of insulin
- The correct doses and types of medication.
- Your right exercise pan
- The number of meals and snacks you should take in a day
It is important to note that a CGM cannot replace a traditional glucose monitor. You will still need to measure your glucose levels daily to see if the monitor is accurate. Most monitors still require a finger stick, and you should replace your sensor every seven days.
You can also link your continuous glucose monitor with your insulin pump if you use one. This way, as with other finger prick methods, you will not need to calibrate your insulin pump manually.
Unlike traditional glucose meters, a CGM device controls blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. The system is programmed to show your highs and lows throughout the week. A CGM system can help you:
- Track the high sugar levels between meals
- Record the low overnight blood glucose levels that may go undetected
- Help you see how your diet and exercise plan affect you
- Show when you have early morning glucose spikes
- Help you see how your treatment plan works daily
Who Should Use A CGM?
You can only use a CGM device if your doctor recommends it. Doctors often recommend a CGM device when:
- You have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes
- You have central high and low in your sugar levels with no clear reason
- You are using an insulin pump
- Your blood sugar levels are very high (Hyperglycemia) or when they are too low (Hypoglycemia)
Children can use CGM devices above two years old and adults. Additionally, you can pair the FDA-approved apps with your CGM device, where information on a patient’s glucose level is shared immediately. The apps are expected to help caregivers and parents who cannot always be in the same place as someone with diabetes.
What Are The Limits Of A CGM Device?
 Much research is on making a CGM device more accurate and easy to use. You will still need to use a finger-stick test at least twice daily to check its accuracy. Most doctors do not only rely on the CGM when planning to change the insulin dosage. They must confirm the blood sugar levels using the finger-stick test.
Much research is on making a CGM device more accurate and easy to use. You will still need to use a finger-stick test at least twice daily to check its accuracy. Most doctors do not only rely on the CGM when planning to change the insulin dosage. They must confirm the blood sugar levels using the finger-stick test.
A CGM device is also more expensive than a traditional glucose meter. You can check with your insurance plan to see if they will cover the cost of the device.
Do you want to learn how to manage type 2 diabetes better? Visit Columbia Medical Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems (CGMS). We are experts in continuous glucose monitoring devices to help you manage Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes with no finger sticks!





 We are experts in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems (CGMS). Our CGM devices will help you efficiently manage Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes with No Fingersticks!. Abbot’s Freestyle Libre System will track the glucose levels in your blood and help you determine how much insulin you will need and when you will need it!
We are experts in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems (CGMS). Our CGM devices will help you efficiently manage Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes with No Fingersticks!. Abbot’s Freestyle Libre System will track the glucose levels in your blood and help you determine how much insulin you will need and when you will need it!